Value Stream Mapping
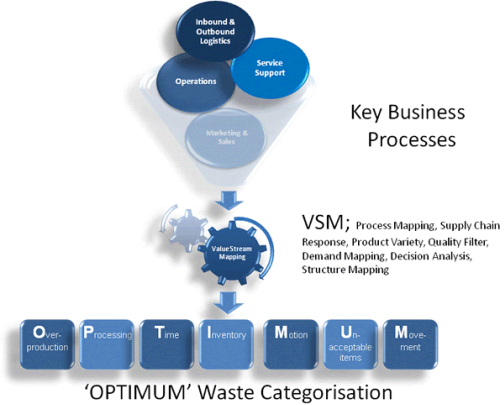
Value Stream Mapping Overview
* Value Stream Mapping (VSM) is a technique that can be employed to not only provide a visual representation of a procedure, but also have the potential to identify significant savings in the way in which the process is organised and performed.
* Value Stream Mapping technique is often associated with Lean programmes to identify opportunities for improvement in lead time, logistics, supply chain, service related industries, healthcare, software development, and product development. It is used to analyse the flow of materials and information currently required to bring a product or service to a customer. The technique originated in Toyota, where it is known as "Material and Information Flow Mapping".
* Valued added activity being; adding value to a product or service. Something the customer is willing to pay for, such as higher performance, more features, quicker or more responsive delivery. Non‐value adding activities being; not adding value to the product or service. Something the customer is unwilling to pay for, such as a business process with no competitive advantage, activities which result in mistakes, errors or non‐conformance. It can include activities such as training.
* Organisations are full of processes, not only manufacturing processes but processes for purchasing, warehousing, handling orders, etc. These processes can involve moving and manipulating data and information (e.g. service industries) as much as material (e.g. manufacturing industries). They can also involve various departments and specialists in completing tasks and activities, making decisions, filling out forms, filing and retrieving information. The processes can also involve complex parallel and serial activities interconnected and dependant of tasks being completed satisfactorily. Very often these processes have evolved as the organisation has grown, sometimes keeping pace, sometimes overwhelmed by the sheer size of the organisational growth.
* To solve growth problems ‐ such as maintaining the throughput, quick fix solutions may be used e.g. increasing the labour resource rather than improving or overhauling the process. Sometimes this can just make the situation worse. (If it takes one man one day to dig a hole ‐ then one hundred men can dig the hole in one hundredth of the time!!!). In other words increasing the labour resource again will not necessarily result in quicker throughput. Some jobs just cannot be done by more than one person.
* Knowing how to identify processes and distinguish from procedure
* Collecting data for Value Stream mapping
* Applying the recognised industry standard analysis technique associated with Value Stream mapping.
* Knowing the benefits of 'Value Stream Mapping'
* Knowing how to form the value stream team
* Understanding customer demand associated with VSM
* Knowing how to develop the value stream information system
* Using the Value stream mapping symbols
* Knowing how to construct the 'Current State Map'
* Knowing how to Construct the 'Future State Map'
* Establishing 'Future State' implementation strategy development and deployment
* Identifying opportunities and problem areas within existing business Value Streams
* Modelling and assessing the impact of any proposed changes to a key process.
* Providing the opportunity to make real major financial saving through QM&T's pre and post course supported assignment scheme
* Value Stream mapping software
* Completing a Value Stream Mapping initiative
* Lean thinking
* Process re‐engineering / process improvement The 8 steps of Value Stream Mapping
* Team member roles and responsibilities
* Value stream mapping techniques
* Identifying and eliminating non‐value activities
* Understanding the change implications
Buy Now
